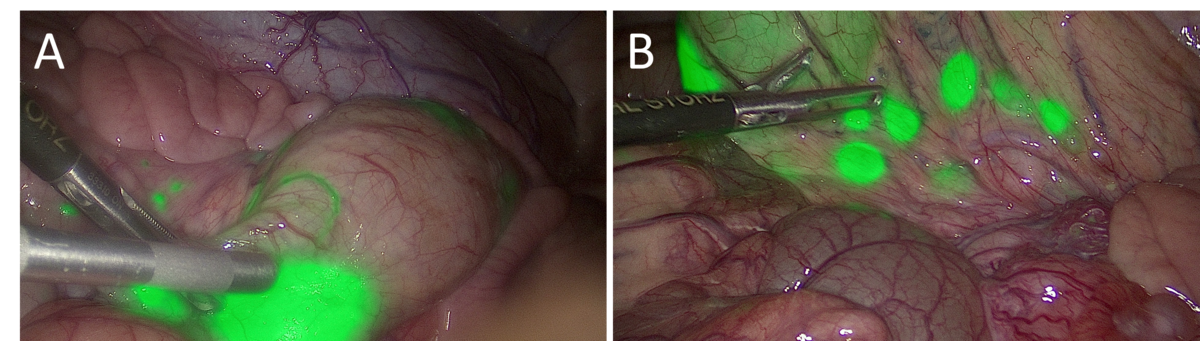
NIR microparticles for minimally invasive surgery
The aim of this sub-project is to conduct applied research that will result in formulations of microparticles loaded with near-infrared (NIR) quantum dots (QD). Additionally, tumour areas in phantoms and model systems up to clinical proof of concept (PoC) for gastrointestinal (GI) tract tumours are to be marked. The initial objective of this sub-project is applied research to qualify the essential properties of NIR-QD-loaded microparticles with regard to their suitability for detection in minimally invasive surgical procedures. The second objective is to use these microparticles for endoscopic marking in test systems with a visualisation capability of up to 10 days, including the generation of high-resolution videos for NIR imaging of the markings and the export of these data for training an artificial intelligence (AI) system. The final objective of the sub-project is to provide the clinical PoC for NIR marking in minimally invasive surgery. The generated videos will serve as a database for training an AI system for video analysis in fluorescence-assisted surgical navigation.