Step-by-Step
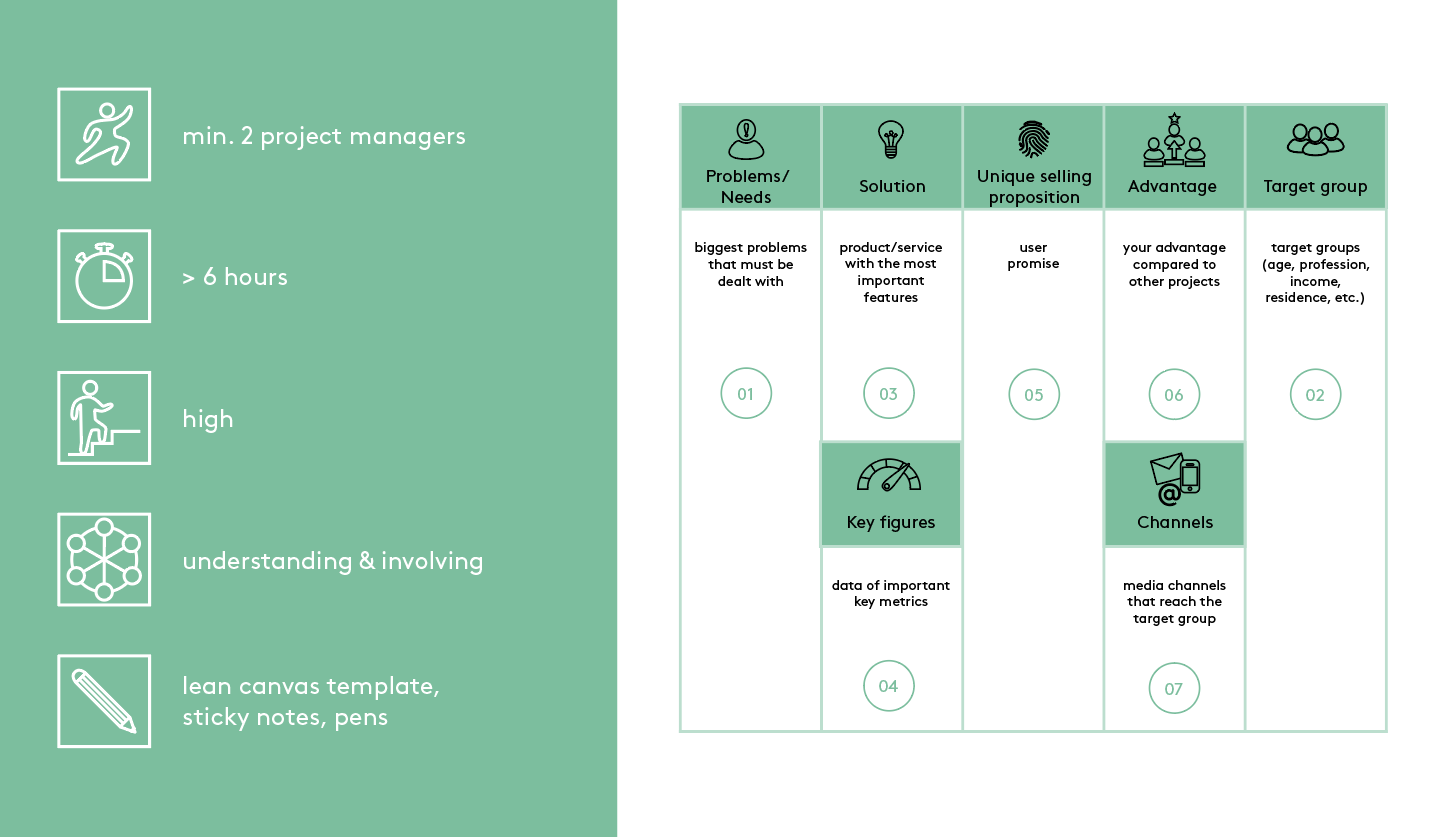
The Lean Canvas contains several fields with different aspects to strategically align your project. The fields listed here should be filled in one after the other. Use data-based information for this.
1. What are the existing and relevant problems or needs in society? Define the biggest problems to be addressed at the beginning.
2. Who is affected by these problems or needs? What target group(s) can you identify (age, income, location, etc.)? You can use the Persona method for a more in-depth discussion of the target group.
3. How can the problems and needs be solved for your target group? Develop a possible solution for each of these problems or needs.
4. How can you measure the success of your solution? Define key metrics of the identified problems or needs that will make your project measurable later, e.g. 30% of people living alone are over 60 years old.
5. What is your unique selling proposition? Define the user promise of your solution offered to your target audience(s).
6. What (competitive) advantage do you have over other projects/providers of similar products or services? Define what is not so easy to imitate in your project, e.g. a large network.
7. What channels can you use to reach your target group(s)? Collect different media for this, e.g. radio, newspaper, Facebook, etc.
8. Afterwards, discuss which conclusions you can draw from the information in the Lean Canvas and which subsequent steps you need to focus on in order to achieve the solutions.
More about the tool
Testimonial



